What’s the Impact of Diet Plans on Longevity and Aging?

Introduction
Did you know that what you eat could be the key to a longer, healthier life? Diet plays a crucial role in how we age and how long we live. More and more people are turning to special eating plans to try to extend their lives. But here’s the thing: not all diets are equal when it comes to aging. Some might help you live longer, while others might not make much difference at all.
In this post, we’ll explore how different diet plans affect longevity and aging. We’ll look at popular diets, important nutrients, and how food choices can impact age-related diseases. By the end, you’ll have a better idea of how to eat for a longer, healthier life.
Understanding Longevity and Aging
Before we dive into specific diets, let’s talk about what longevity and aging really mean.
What Are Longevity and Aging?
Longevity is how long a person lives. It’s about the number of years you’re alive. Aging, on the other hand, is the process of getting older. It involves changes in your body over time.
What Affects How Long We Live?
Many things can influence how long we live:
- Genes
- Environment
- Lifestyle choices
- Access to healthcare
- Diet and nutrition
While we can’t control all of these factors, diet is one area where we have a lot of power to make positive changes.
How Does Diet Affect Aging at the Cellular Level?
What we eat can actually change how our cells age. Here’s how:
- Oxidative stress: Some foods can help fight damage from harmful molecules called free radicals.
- Inflammation: Certain diets can reduce inflammation in the body, which is linked to many age-related diseases.
- DNA repair: Some nutrients help our body fix damage to our DNA, which can slow down aging.
- Telomere length: Telomeres are like caps on the ends of our DNA. Some diets might help keep these caps longer, which is linked to living longer.
By choosing the right foods, we can potentially slow down the aging process at a cellular level. This is why anti-aging nutrition is becoming such a hot topic in health and wellness circles.
Popular Diet Plans and Their Impact on Aging
Let’s explore some well-known diets and how they might help us live longer, healthier lives.
Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is often praised for its potential to boost longevity. But what makes it special?
Key components of the Mediterranean diet:
- Lots of fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains
- Olive oil as the main fat source
- Moderate amounts of fish and poultry
- Limited red meat
- Optional moderate consumption of red wine
Research on longevity: Studies have shown that people who follow the Mediterranean diet tend to live longer. For example, a study published in the British Medical Journal found that adherence to this diet was associated with longer telomeres, which are linked to longevity.
Potential anti-aging benefits:
- Rich in antioxidants, which fight cellular damage
- High in healthy fats that support brain health
- Emphasizes whole foods, which provide essential nutrients
- May reduce inflammation, a key factor in aging

Calorie Restriction
Calorie restriction is a more extreme approach to anti-aging nutrition. It involves eating fewer calories while still getting all necessary nutrients.
How it works: The idea is that by eating less, you put less stress on your body, potentially slowing down the aging process.
Studies on lifespan extension: Research on animals has shown promising results. For example, studies on mice have found that calorie restriction can increase lifespan by up to 50%.
Challenges for humans:
- It can be difficult to maintain long-term
- May lead to nutrient deficiencies if not done carefully
- Could cause side effects like feeling cold or having less energy
While calorie restriction shows promise, it’s not for everyone. Always consult a healthcare professional before trying such a restrictive diet.
Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting has gained popularity as a potential longevity diet plan. It’s not about what you eat, but when you eat.
Types of intermittent fasting:
- Time-restricted feeding (e.g., eating only within an 8-hour window each day)
- Alternate-day fasting
- 5:2 diet (eating normally for 5 days, restricting calories for 2 days)
How it may influence longevity:
- Promotes cellular repair processes
- May improve insulin sensitivity
- Could reduce inflammation
Potential risks and benefits:
- Benefits: Weight loss, improved metabolic health
- Risks: Overeating during eating periods, potential nutrient deficiencies

Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets, ranging from vegetarian to vegan, have been associated with longer lifespans in some studies.
Types of plant-based diets:
- Vegetarian: Excludes meat
- Vegan: Excludes all animal products
- Flexitarian: Mostly plant-based but occasionally includes meat
Nutrient considerations: When following a plant-based diet, it’s important to ensure you’re getting enough:
- Protein
- Vitamin B12
- Iron
- Zinc
- Omega-3 fatty acids
Research on longevity: Some studies suggest that plant-based diets may reduce the risk of chronic diseases and promote longevity. For example, a study in the Journal of the American Heart Association found that plant-based diets were associated with a lower risk of all causes of mortality.
Key Nutrients and Compounds for Longevity
While overall dietary patterns are important, certain nutrients play a crucial role in healthy aging. Let’s explore some of these key players:
Antioxidants
Antioxidants are compounds that help combat oxidative stress, a major contributor to aging.
Role in longevity:
- Neutralize harmful free radicals
- Protect cells from damage
- May slow down the aging process
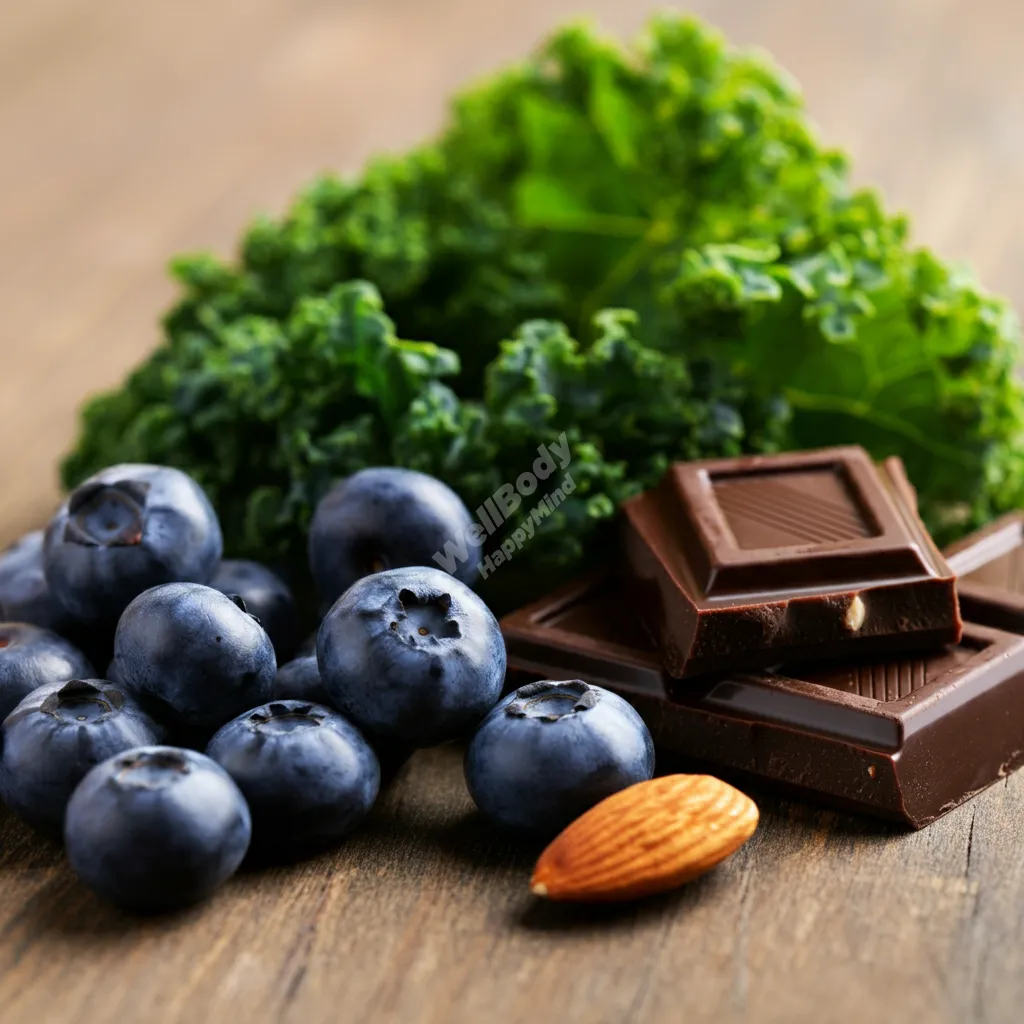
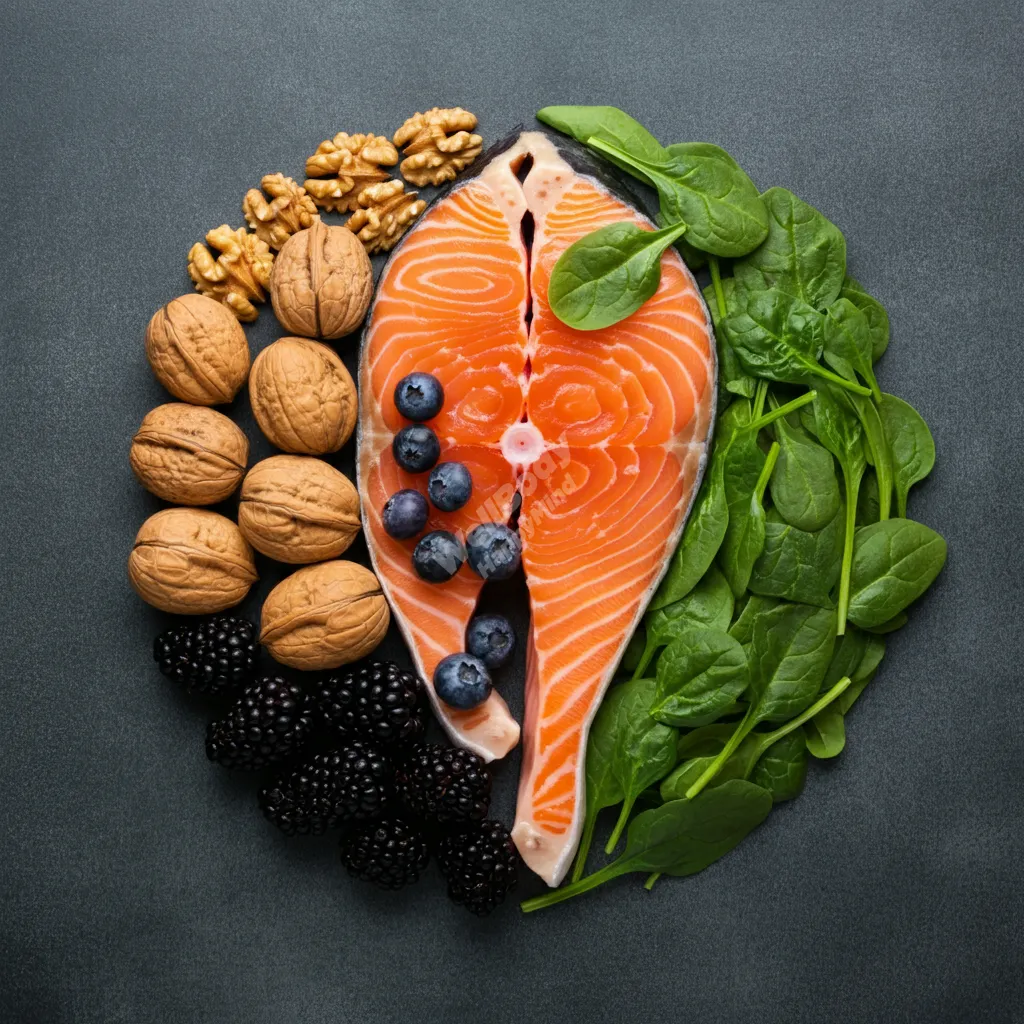
Food sources rich in antioxidants:
- Berries (blueberries, strawberries, goji berries)
- Dark leafy greens (spinach, kale)
- Nuts (pecans, walnuts)
- Dark chocolate
- Green tea

Omega-3 Fatty Acids
These essential fats are crucial for brain health and reducing inflammation.
Benefits for longevity:
- Support cognitive function as we age
- Reduce inflammation throughout the body
- May help protect against heart disease
Best dietary sources:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Flaxseeds and chia seeds
- Walnuts
- Algae and algae-based supplements (for vegetarians/vegans)
Fiber
Fiber is often overlooked, but it’s vital for gut health and longevity.
Impact on aging:
- Supports a healthy gut microbiome
- May reduce risk of chronic diseases
- Helps maintain healthy weight and blood sugar levels
High-fiber foods to include:
- Whole grains (oats, quinoa, brown rice)
- Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas)
- Fruits (apples, pears, berries)
- Vegetables (broccoli, carrots, Brussels sprouts)
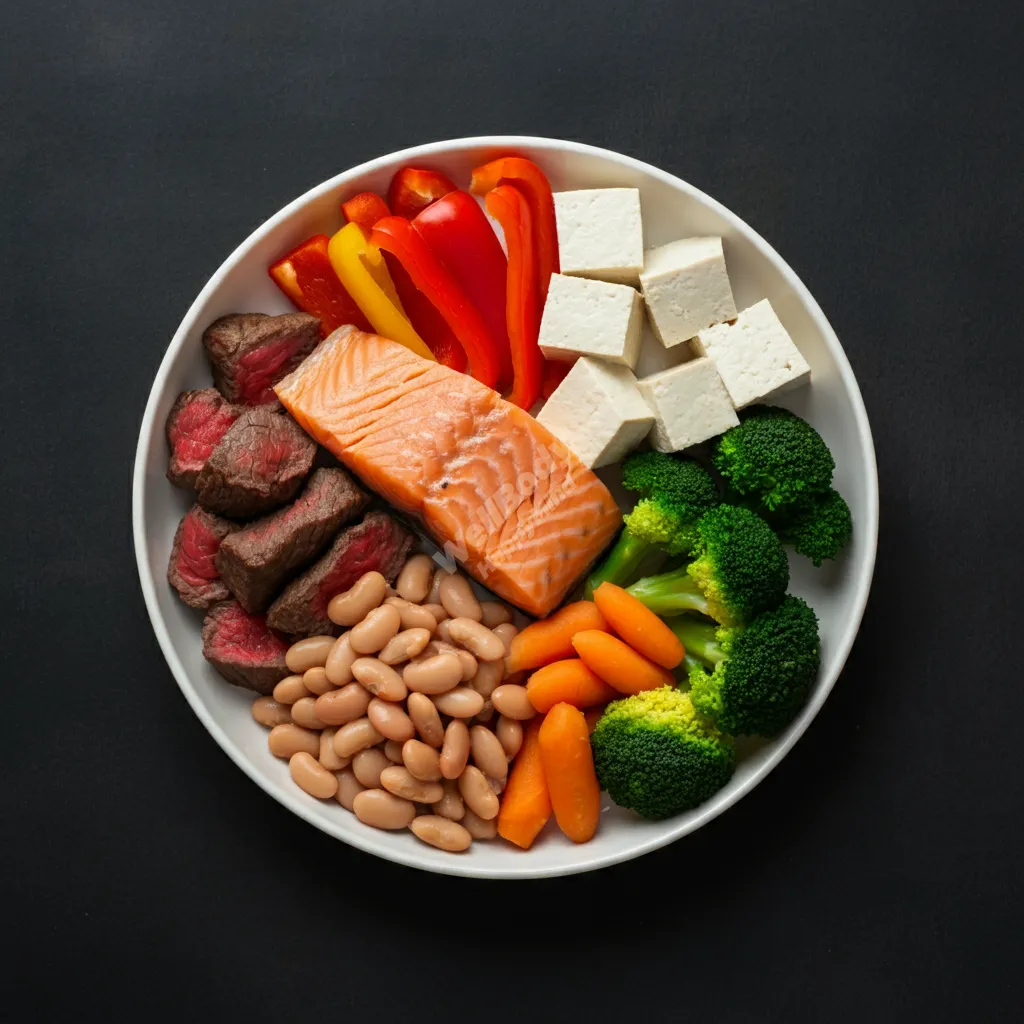
Protein
Adequate protein intake is crucial for maintaining muscle mass as we age.
Importance for longevity:
- Preserves lean muscle mass
- Supports immune function
- Aids in recovery and repair of tissues
Balancing protein intake:
- Aim for a mix of plant and animal proteins (if not vegetarian/vegan)
- Include protein at each meal
- Consider protein quality (complete vs. incomplete proteins)

The Role of Dietary Patterns in Age-Related Diseases
Now, let’s explore how different diets can impact common age-related health concerns:
Heart Disease
How diets affect cardiovascular health:
- Mediterranean diet: Rich in heart-healthy fats and antioxidants
- DASH diet: Emphasizes low-sodium foods to support healthy blood pressure
- Plant-based diets: May lower cholesterol and reduce inflammation
Key dietary factors:
- Limit saturated and trans fats
- Increase intake of omega-3 fatty acids
- Focus on whole, unprocessed foods
Type 2 Diabetes
Dietary approaches for prevention and management:
- Low glycemic index diets: Help control blood sugar levels
- Mediterranean diet: May improve insulin sensitivity
- Plant-based diets: Can aid in weight management, a key factor in diabetes prevention
Important considerations:
- Control portion sizes
- Choose complex carbohydrates over simple sugars
- Include lean proteins and healthy fats to balance meals
Cognitive Decline
Diets associated with better brain health in aging:
- MIND diet: Combines elements of Mediterranean and DASH diets, specifically for brain health
- Mediterranean diet: Rich in nutrients that support cognitive function
- Ketogenic diet: Some research suggests potential benefits for neurological health
Key dietary factors:
- Include fatty fish for omega-3s
- Eat plenty of colorful fruits and vegetables
- Consider including nuts and seeds for healthy fats and antioxidants

Implementing a Longevity-Focused Diet Plan
Now that we’ve explored various longevity diet plans and key nutrients, let’s discuss how to put this knowledge into practice.
Personalization is Key
Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to anti-aging nutrition. What works best for you depends on:
- Your current health status
- Personal food preferences
- Lifestyle factors
- Genetic predispositions
It’s crucial to find a dietary approach that you can maintain long-term. The most effective longevity diet is one that you can stick with consistently.
Gradual Changes for Sustainable Results
Instead of making drastic changes overnight, consider implementing small, manageable adjustments to your diet. This approach is more likely to lead to lasting habits.
Tips for incorporating longevity-promoting foods:
- Add one new vegetable to your diet each week
- Swap refined grains for whole grains in one meal a day
- Include a serving of fatty fish in your menu twice a week
- Experiment with meatless meals once or twice a week
- Incorporate a handful of nuts or seeds into your daily snacks
Combining Diet with Other Lifestyle Factors
While diet plays a crucial role in longevity, it’s important to remember that it’s just one piece of the puzzle. For optimal results, combine your longevity diet plan with:
- Regular physical activity
- Adequate sleep (7-9 hours per night for most adults)
- Stress management techniques (like meditation or yoga)
- Social connections and meaningful relationships

Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
While focusing on longevity through diet can be beneficial, there are some important considerations to keep in mind:
Risks of Extreme Dieting
Extreme approaches to diet, even when done with good intentions, can sometimes do more harm than good. Potential risks include:
- Nutrient deficiencies
- Disordered eating patterns
- Excessive stress or anxiety around food choices
Importance of Balanced Nutrition
While certain foods and nutrients may have longevity-promoting properties, it’s crucial to maintain a balanced diet. Overemphasis on specific “superfoods” at the expense of overall dietary variety can lead to nutritional imbalances.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals
Before making significant changes to your diet, especially if you have existing health conditions, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can help you:
- Assess your current health status
- Identify potential risks or contraindications
- Develop a personalized plan that aligns with their health goals
Conclusion
The impact of diet plans on longevity and aging is a fascinating and evolving area of research. While there’s no magic bullet for eternal youth, the food choices we make every day can significantly influence how we age and how long we live.
Key takeaways:
- Different dietary approaches, from the Mediterranean diet to intermittent fasting, offer various potential benefits for longevity.
- Specific nutrients like antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and protein play crucial roles in healthy aging.
- Our diet can influence the risk of age-related diseases like heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and cognitive decline.
- The best longevity diet is one that is personalized, sustainable, and combined with other healthy lifestyle factors.
As you consider implementing changes to your diet for longevity, remember to start small, focus on whole foods, and listen to your body. Healthy aging isn’t just about adding years to your life—it’s about adding life to your years.
We encourage you to take the knowledge you’ve gained from this article and use it to make informed, sustainable dietary choices. Start by incorporating one or two longevity-promoting habits into your routine this week. Your future self will thank you!
Remember, the journey to a longer, healthier life is a marathon, not a sprint. Be patient with yourself, celebrate small victories, and enjoy the process of nourishing your body for the long haul.
What small step will you take today towards a diet that supports longevity and healthy aging?




