7 Key Strategies for Reducing the Risk of Infectious Diseases

Introduction
Did you know that infectious diseases account for millions of deaths worldwide each year? These illnesses, caused by harmful microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, and parasites, can spread quickly and have a significant impact on our health and well-being. The good news is that many infectious diseases are preventable, and by adopting some simple strategies, we can greatly reduce our risk of falling ill.
In this post, we’ll explore 7 key strategies for reducing the risk of infectious diseases. By incorporating these healthy habits for disease prevention into your daily routine, you can protect yourself and your loved ones from a wide range of illnesses. Let’s dive in and discover how you can boost your defenses against infectious diseases!
1. Practice Good Hand Hygiene
One of the most effective infectious disease prevention strategies is proper hand hygiene. Our hands are like magnets for germs, picking them up from everything we touch throughout the day. By washing our hands regularly, we can significantly reduce the risk of spreading harmful microorganisms.
Why is handwashing so important? It’s simple: clean hands save lives. Proper handwashing can prevent about 30% of diarrhea-related illnesses and 20% of respiratory infections. That’s a big impact from such a simple habit!
Here’s how to wash your hands properly:
- Wet your hands with clean, running water
- Apply soap and lather well
- Scrub all surfaces of your hands for at least 20 seconds
- Rinse thoroughly under running water
- Dry your hands using a clean towel or air dry
When should you wash your hands? Here’s a quick list:
- Before, during, and after preparing food
- Before eating
- After using the toilet
- After changing diapers or cleaning up a child who has used the toilet
- After blowing your nose, coughing, or sneezing
- After touching an animal, animal feed, or animal waste
- After handling pet food or pet treats
- After touching garbage
Can’t access soap and water? Hand sanitizers can be a good alternative. Look for an alcohol-based sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol content. While not as effective as handwashing, especially when hands are visibly dirty, sanitizers can still help reduce the spread of germs when soap and water aren’t available.
Remember, good hand hygiene is one of the simplest yet most powerful tools in reducing the risk of infectious diseases. Make it a habit, and you’ll be taking a big step towards better health!
2. Get Vaccinated
Vaccination is one of the most crucial infectious disease prevention strategies available to us. Vaccines work by stimulating our immune system to produce antibodies, providing protection against specific diseases without us having to get sick first.
The importance of vaccines in preventing infectious diseases cannot be overstated. They have helped eradicate smallpox and have significantly reduced the incidence of many other life-threatening illnesses.
Here’s a table of some common vaccines and the diseases they prevent:
| Vaccine | Disease(s) Prevented |
|---|---|
| MMR | Measles, Mumps, Rubella |
| DTaP | Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis |
| Polio | Poliomyelitis |
| Flu shot | Influenza |
| HPV | Human Papillomavirus |
| Hepatitis B | Hepatitis B |
It’s important to address vaccine hesitancy, which is often based on misinformation. Vaccines are safe and effective. They undergo rigorous testing before approval, and their benefits far outweigh any potential risks. Serious side effects are extremely rare, while the diseases they prevent can cause severe complications or even death.
Staying up-to-date with vaccinations is crucial for maintaining immunity. Some vaccines require booster shots, while others (like the flu shot) are recommended annually. Always consult with your healthcare provider about which vaccines you need based on your age, health status, and lifestyle.
Remember, by getting vaccinated, you’re not just protecting yourself. You’re also contributing to community immunity, helping to protect those who can’t be vaccinated due to age or health conditions. It’s a powerful way to reduce the risk of infectious diseases for everyone.
3. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle

A healthy lifestyle is a cornerstone of reducing the risk of infectious diseases. It’s one of the most effective ways to boost your immune system naturally, helping your body fight off potential infections.
Balanced Diet: What you eat plays a crucial role in boosting immunity. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats provides your body with essential nutrients. Vitamins C and D, zinc, and antioxidants are particularly important for immune function. Try to include a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables in your meals to ensure you’re getting a wide range of nutrients.
Regular Exercise: Physical activity is not just good for your muscles and heart; it’s also great for your immune system. Moderate exercise, like brisk walking or cycling for 30 minutes a day, can help boost your body’s defense mechanisms. It improves circulation, reduces stress, and may even help flush bacteria out of your lungs and airways.
Adequate Sleep: Never underestimate the power of a good night’s sleep! During sleep, your body produces and distributes key immune cells. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to keep your immune system in top shape.
Stress Management: Chronic stress can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. Here are some effective stress management techniques:
- Deep breathing exercises
- Meditation or mindfulness practices
- Regular physical activity
- Engaging in hobbies or activities you enjoy
- Connecting with friends and family
- Limiting exposure to stressful news or social media
By incorporating these healthy habits for disease prevention into your daily routine, you can significantly strengthen your body’s natural defenses. Remember, a healthy lifestyle is not just about preventing illness; it’s about feeling your best every day!
4. Practice Safe Food Handling

Safe food handling is a crucial aspect of reducing the risk of infectious diseases, particularly foodborne illnesses. These illnesses can range from mild discomfort to severe conditions requiring hospitalization. By following proper food safety practices, you can significantly reduce your risk of contracting these infections.
The importance of food safety cannot be overstated. According to the World Health Organization, an estimated 600 million people fall ill after eating contaminated food each year. That’s nearly 1 in 10 people worldwide!
Here are some essential tips for safe food preparation and storage:
- Wash hands thoroughly before and after handling food
- Clean all surfaces and utensils before and after use
- Separate raw and cooked foods to avoid cross-contamination
- Cook foods to the right temperature (use a food thermometer)
- Chill leftovers promptly (within 2 hours of cooking)
- Thaw frozen foods in the refrigerator, not on the counter
- Rinse fruits and vegetables before eating
- Check expiration dates and discard expired foods
Common foodborne pathogens include Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria. To avoid these:
- Cook meats thoroughly, especially poultry and ground beef
- Avoid raw or unpasteurized milk and cheeses
- Wash hands after handling raw eggs
- Keep ready-to-eat foods refrigerated
Remember, proper food handling is one of the most effective infectious disease prevention strategies you can practice at home. By following these guidelines, you’re not just protecting yourself, but also your family and anyone else who eats the food you prepare.
Stay vigilant in the kitchen, and you’ll go a long way in keeping foodborne illnesses at bay!
5. Stay Informed and Follow Public Health Guidelines

In our ever-changing world, staying informed about current health issues and following public health guidelines is crucial for reducing the risk of infectious diseases. This strategy is particularly important during disease outbreaks or pandemics.
The importance of staying updated on current health advisories cannot be overstated. Public health guidelines are designed by experts who have access to the latest scientific data and understanding of disease spread. By following these guidelines, you’re leveraging this expertise to protect yourself and your community.
Here are some reliable sources for health information:
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Your local health department
- Reputable medical institutions (e.g., Mayo Clinic, Johns Hopkins)
- Government health websites (e.g., health.gov)
When following guidelines during disease outbreaks or pandemics:
- Stay calm and rational. Panic can lead to poor decision-making.
- Follow official recommendations for social distancing, mask-wearing, or other protective measures.
- Be prepared, but avoid hoarding supplies.
- Fact-check information before sharing it with others.
- Adapt your routines as necessary to comply with current guidelines.
Remember, public health is a collective effort. By staying informed and following guidelines, you’re not just protecting yourself, but also contributing to the overall health of your community. This is especially important for protecting vulnerable populations who may be at higher risk from infectious diseases.
In the age of information, knowledge truly is power. Use it wisely to keep yourself and others safe!
6. Practice Respiratory Hygiene
Respiratory hygiene is a crucial component of infectious disease prevention strategies, especially when it comes to illnesses that spread through respiratory droplets, such as the common cold, flu, and COVID-19.
The importance of covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing cannot be overstated. This simple act can significantly reduce the spread of infectious droplets in the air, protecting those around you from potential illness.
Here’s how to practice good respiratory hygiene:
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue when you cough or sneeze.
- If you don’t have a tissue, cough or sneeze into your elbow, not your hands.
- Dispose of used tissues immediately in a closed bin.
- Wash your hands thoroughly after coughing, sneezing, or blowing your nose.
Proper use of tissues:
- Use a clean tissue each time you need to cough or sneeze.
- Dispose of the tissue immediately after use.
- Don’t store used tissues in your pockets or on surfaces.
When and how to use face masks:
- Wear a mask in public settings, especially when social distancing is difficult.
- Ensure the mask covers both your nose and mouth.
- Don’t touch the front of the mask while wearing it or when removing it.
- Wash reusable masks regularly or dispose of single-use masks properly.
Remember, face masks are most effective when everyone wears them. They help prevent the wearer from spreading respiratory droplets and offer some protection against inhaling droplets from others.
By practicing good respiratory hygiene, you’re taking an active role in reducing the risk of infectious diseases for yourself and those around you. It’s a simple yet powerful way to contribute to public health!
7. Maintain a Clean Environment
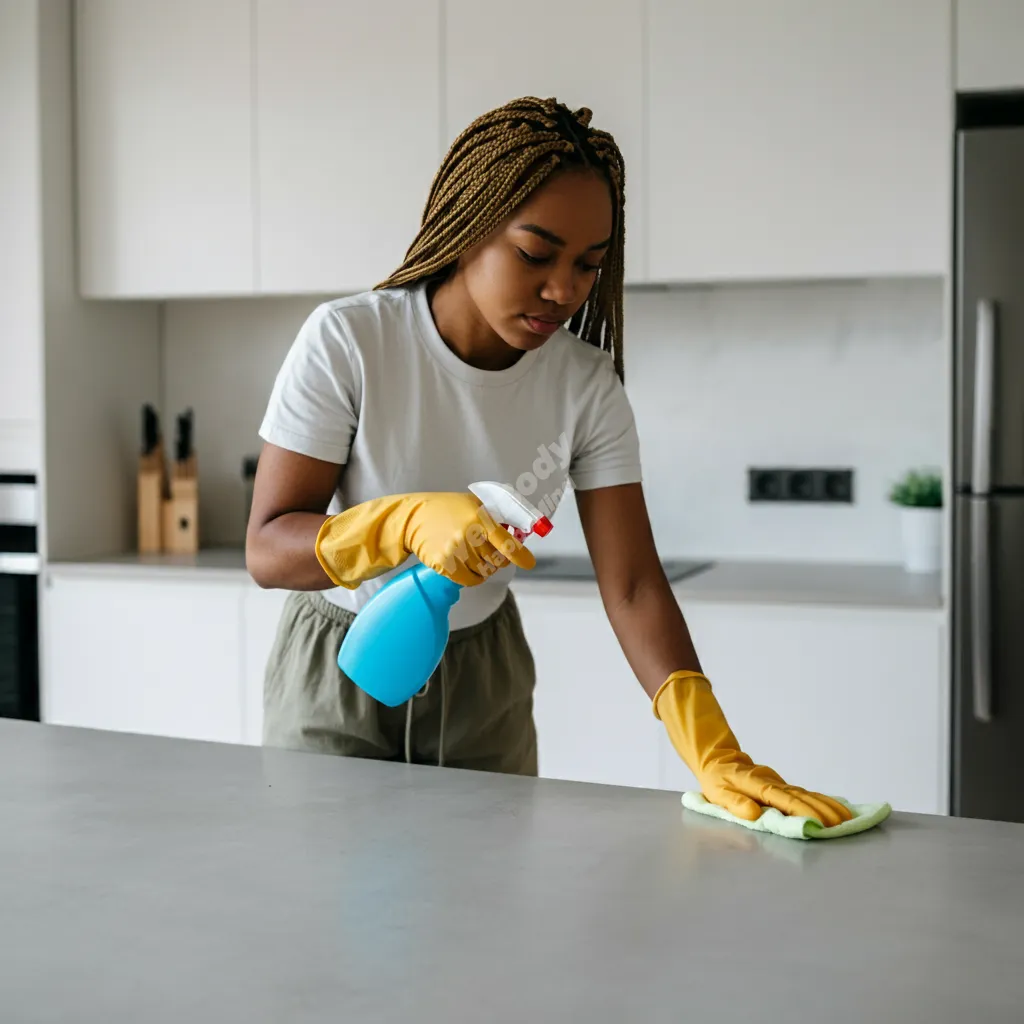

Creating and maintaining a clean environment is a key strategy in reducing the risk of infectious diseases. A clean space not only looks and feels good but also plays a crucial role in preventing the spread of harmful microorganisms.
The importance of regular cleaning and disinfection cannot be overstated. While cleaning removes visible dirt and grime, disinfecting actually kills germs on surfaces. Both are essential for a truly hygienic environment.
Here’s a list of high-touch surfaces to focus on:
- Doorknobs and handles
- Light switches
- Countertops
- Keyboards and computer mice
- Phones and tablets
- Remote controls
- Faucet handles
- Toilet flush handles
- Stair railings
- Appliance handles (refrigerator, microwave, etc.)
When it comes to safe and effective cleaning products, you have several options:
- EPA-registered disinfectants
- Diluted household bleach solutions (follow manufacturer’s instructions for proper dilution)
- Alcohol solutions with at least 70% alcohol
Remember to always follow the product instructions and wear gloves when cleaning.
Proper ventilation also plays a significant role in reducing airborne transmission of infectious agents. Here’s why it’s important:
- It helps remove and dilute airborne contaminants
- It can reduce the concentration of viral particles in the air
- It helps control humidity, which can affect virus survival
To improve ventilation:
- Open windows when weather permits
- Use fans to increase air circulation
- Ensure your HVAC system is properly maintained
By maintaining a clean environment and ensuring good ventilation, you’re creating an additional layer of protection against infectious diseases. It’s an essential part of a comprehensive approach to healthy habits for disease prevention.
Conclusion
As we’ve explored in this post, reducing the risk of infectious diseases is not just about one single action, but a combination of healthy habits and prevention strategies. Let’s recap the 7 key strategies we’ve discussed:
- Practice Good Hand Hygiene
- Get Vaccinated
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
- Practice Safe Food Handling
- Stay Informed and Follow Public Health Guidelines
- Practice Respiratory Hygiene
- Maintain a Clean Environment
Each of these strategies plays a crucial role in protecting your health, but their true power lies in combining them. By implementing all these practices in your daily life, you create a robust defense system against infectious diseases.
It’s important to remember that disease prevention is an ongoing process. It requires consistent effort and mindfulness, but the benefits far outweigh the effort. By adopting these habits, you’re not just protecting yourself, but also contributing to the health and wellbeing of your community.
We encourage you to incorporate these practices into your daily routine. Start small if you need to – perhaps by focusing on improving your hand hygiene or making a commitment to stay up-to-date with your vaccinations. Over time, try to implement more of these strategies until they become second nature.
Remember, your health is in your hands. By taking these proactive steps, you’re empowering yourself to lead a healthier, more resilient life. Let’s work together to create a world where infectious diseases have less power over our lives.
Stay healthy, stay informed, and keep practicing these infectious disease prevention strategies. Your body (and those around you) will thank you for it!



